Prerequisites
For an up-to-date list of prerequisites, please see https://www.peersoftware.com/resources/tech-briefs.html?view=document&id=57.
1.Review the prerequisites above before beginning the installation and configuration process.
2.Follow the general PeerLink installation steps that can be found here.
3.Launch the PeerLink Hub Client.
Note: Before you can start the PeerLink Hub interface/client, the PeerLink Hub Service needs to be running. See the installation section for more information.
4.Install your license within the PeerLink Hub. For more information, see the licensing section. You must contact our sales team to request a license which supports NetApp. Unless requested, all licenses that are issued do not include NetApp support by default.
5.Create a new file collaboration job. For more information, visit the section on creating a job.
6.During the job configuration process, one or more participating hosts must be configured to interface with NetApp. To do so, view the Participants page of the File Collaboration Configuration dialog, and add the desired available host to the job. After the host is added to the job, enter the UNC path of the appropriate share on the NetApp Filer to the configured directory of the participant that is to act as a FPolicy Server. Then select NetApp as the participant's configured Event Detector. An example is shown below. As a result of the selection, a configuration dialog will be displayed requesting additional configuration for the FPolicy Server. The only mandatory field is for the local path. The rest of the dialog represents Advanced FPolicy Configuration.
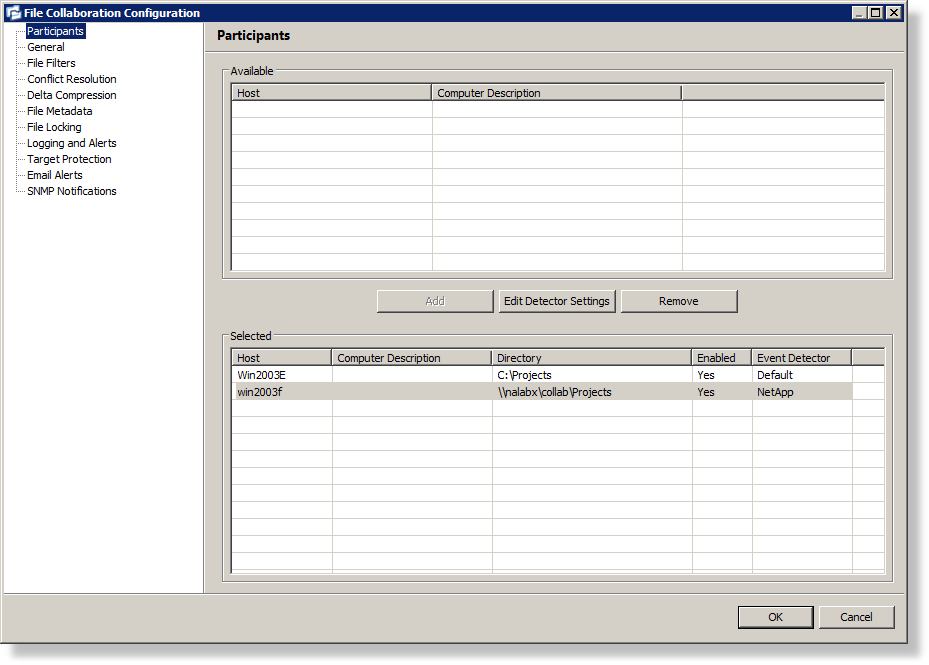
Image 1
7.In order for a file collaboration job to be able to detect files that are already opened, a local mapping to the CIFS share on the NetApp device is required. By default, PeerLink will automatically look this up. If necessary, you can also enter your own. This local mapping should not include any sub-folders for the root UNC path. This local path must be entered into the NetApp Options dialog for each participant (as highlighted in Step 7). An example is listed below.
Example:
UNC path to NetApp Filer (shown in Image 1 above): \\nalabx\collab\Projects
Local Path (obtained for share "collab" in Image 2 below): C:\vol\nalabx_vol1
Value Entered in NetApp Options (Image 3 below): C:\vol\nalabx_vol1\collab
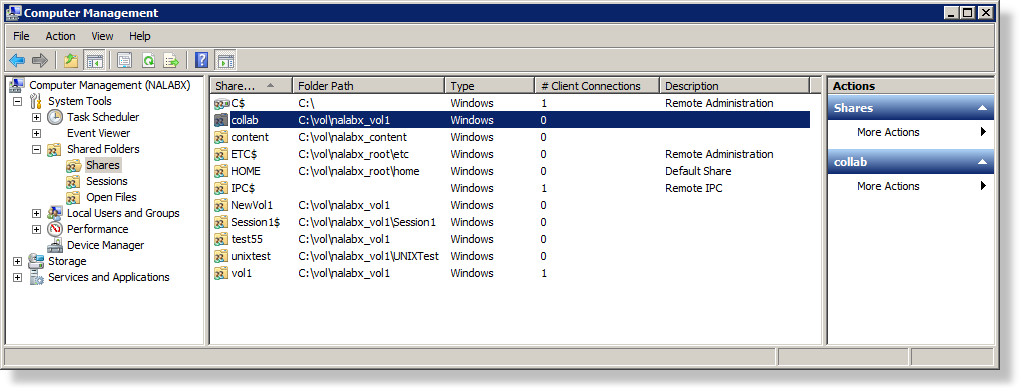
Image 2
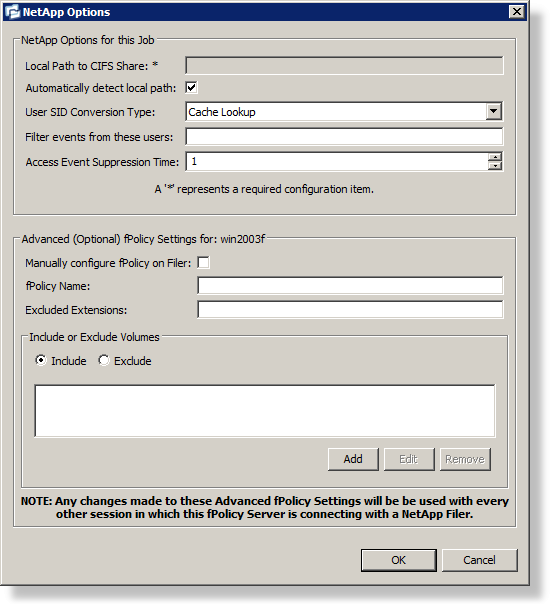
Image 3
8.In addition to setting a local path, some additional host-specific NetApp configuration options are available (as shown in Image 3 above):
Local Path to CIFS Share |
See above. |
Automatically detect local path |
Uncheck this option to manually enter in the local path to the CIFS share on the NetApp device. |
User SID Conversion Type |
By default, events returned from NetApp do not include a user name, but rather the user's SID. If this option is set to Cache Lookup, PeerLink will automatically lookup the user name tied to this SID value the first time it is detected. In the future, PeerLink will then use a cache to quickly convert the SID. |
Filter events from these users |
A comma-separated list of user account names from which events will be ignored. Ideal for filtering out events from backup and/or archival services by filtering on the username under which a backup and/or archival service is running. |
Access Event Suppression Time |
Represents how long an open event will be delayed before being processed. Used to help reduce the amount of real time chatter in several scenarios. The default value is 1 second. A value of 0 will allow for a dynamically changing amount of time that an open event will be delayed based on the load of the system. |